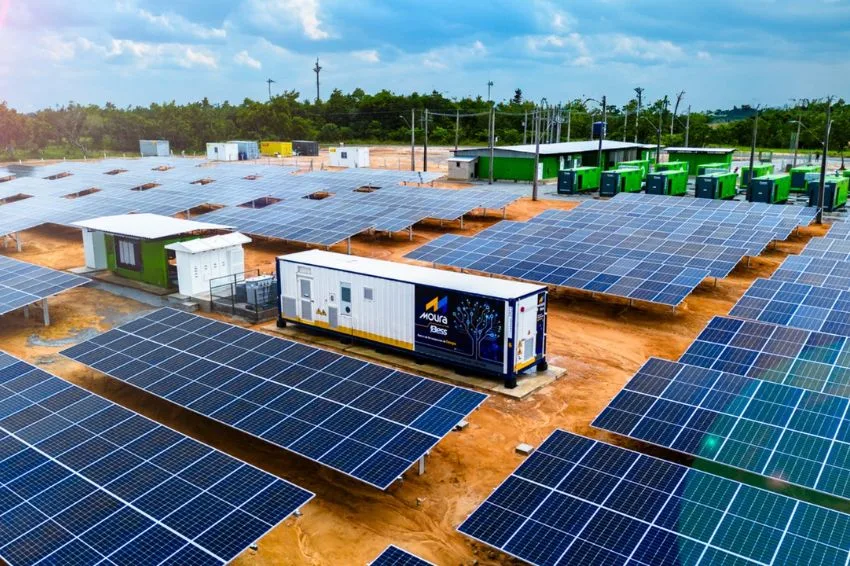
Smart battery banks are sets of one or more packs of commercially available lithium cells for practical use in industrial applications, electrical energy storage systems and renewable energy applications in general.
Smart battery banks have all the electronic circuitry necessary for the protection, control and monitoring of lithium cells, including BMS systems (battery management system) and a communication interface for connection to power converters (DC-AC inverters, for example).
The function of the BMS is to regulate the charging of the battery bank, monitoring the charge and discharge current, voltage and temperature of the bank as a whole and of the individual cells, among other things.
Power converters must be configured according to the characteristics of each battery bank and must communicate, normally via cable, with the BMS system. The main battery bank manufacturers already provide BMS systems configured to be compatible with the main inverters on the market.
Unlike lead acid batteries, which can be directly connected to inverters, which are responsible for controlling their charge and discharge, lithium batteries must necessarily be accompanied by electronic systems for safe operation.
For application in power systems, smart battery banks with one or more packs associated and integrated with BMS circuits are already found on the market, produced by companies such as Tessvolt, BYD and Dyness – brands commercially available in Brazil.
The direct connection of packs From batteries to inverters is complicated because lithium-ion cells are delicate and require load balancing and monitoring of voltage, current and temperature.
For this reason, lithium-ion batteries are necessarily accompanied by BMS electronic circuits that communicate with the inverters through data communication interfaces.
To use batteries, a communication protocol must be used between the bank and the power converter (inverter, for example). The battery bank manufacturer must provide a protocol compatible with the converter that will be used.
Different inverter manufacturers for power system applications have their own protocols for controlling and monitoring equipment, while there are already initiatives to create universal protocols that could be adopted by all manufacturers.















One Response
Is it already being sold?