For some time now, the subject of hybrid inverters has been discussed by manufacturers and installers in the Brazilian photovoltaic market.
The rapid evolution of storage technology applied to solar generation has allowed the creation of increasingly efficient systems. Some manufacturers, such as Fronius, have been working with hybrid inverters for some time.
But before addressing the current status of systems with hybrid inverters in our market, it is necessary to understand what a hybrid inverter is and what the advantages of this type of equipment are.
A hybrid solar inverter is one that also allows the connection of a battery bank, that is, at the same time that it is connected to the distribution network (on-grid) and a solar source, it is also connected to a battery bank. of batteries.
This type of equipment is different from that used in off-grid applications with batteries, where there is no connection to the grid.

Does the hybrid inverter have the same behavior as an on-grid one?
The answer is yes and no, because in terms of operation connected to the distribution network, the hybrid equipment has the same characteristics as a purely on-grid system, interfacing with the electrical grid with the same characteristics.
However, when we talk about application and sizing there are differences. The main function of the hybrid system is known as backup, that is, supplying energy to the loads in the event of a power outage or interruption, or even during times when energy from the power grid is more costly for the user. .
Therefore, it is a more efficient system in terms of managing energy use and its sizing requires a more detailed approach. It is necessary to evaluate the installation's consumption profile, determine the times of greatest consumption and understand who the biggest consumers (loads) are and what the savings and investment expectations are. As it is a more expensive system than the conventional on-grid system, these additional precautions are necessary.
The purpose of this article is to address some features of the hybrid inverter and show the steps to be followed by the Brazilian market so that we can have this type of system as quickly as possible.
As mentioned previously, one of the main features of the hybrid inverter is its backup function. The GEN24 inverter from Fronius, for example, allows two possibilities: the first is what we call PV-point and the second is full-backup.
One of the first applications of GEN24 in a residential installation in Europe has the characteristics shown in the table below.
Table 1: Data from a hybrid inverter system installed in Wels, Austria
|
Installation power |
10.2 kWp |
|
System type |
Installed on roof |
|
Inverter |
Fronius Symo GEN24 Plus 10.0 |
|
Storage Solution |
BYD Battery-Box Premium HVM 22.1 |
|
Approximate annual generation |
10,500 kWh |
|
Commissioning |
March 2019 |

In this system, the full-backup function ensures that all installation loads are powered even in the event of a possible failure in the distribution network. In this situation, even if there is a power outage from the grid, or specific times for work disconnected from the grid, the battery bank is responsible for continuing to supply the loads that are connected there.
When the system is connected to the grid and operating normally, the photovoltaic modules are responsible for charging the batteries or, when there is no solar energy available, it is possible to charge the battery bank using the grid's own energy.
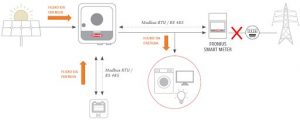
For this type of inverter to function correctly and to be approved in Brazil, it is necessary to use a transfer switch, so that the installation is completely isolated from the electrical grid in case of operation of the inverter disconnected from the grid (in off-grid mode, with full energy supply from batteries). Its use, characteristics and requirements must still be established in standards.
The other backup function of the GEN24 is PV-point. In this configuration, the inverter does not require connection to a battery system. This is an emergency power supply point in the event of a failure in the distribution network.
This power point, or this available dedicated circuit, can be used to supply loads of up to 3 kW, and is completely independent of the connection to the grid, and can work as an isolated point in case the inverter is disconnected from the grid.

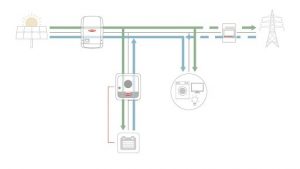
The hybrid inverter will allow intelligent energy management to be maximized, bringing much more efficiency than the conventional on-grid system. In addition to the features already mentioned, the GEN24 has a technology called Multi Flow.
Conventional inverters work with a certain limitation of energy flows, generally allowing circulation in only one direction and without parallelism. In the case of GEN24, the energy direction can be to both sides of the AC/DC coupling and in parallel.
Multi Flow technology allows for more intelligent management of electrical energy use, including adding storage solutions to existing photovoltaic systems with conventional on-grid inverters.
What is needed for this type of system to be used in Brazil?
There are some barriers to be broken at this point. The first of these is the new inverter certification model by INMETRO. This type of inverter, to be approved in a system connected to the grid, must be certified as a “hybrid inverter”.
Currently, INMETRO ordinance 004/2011, which concerns photovoltaic inverters for connection to the grid, does not include hybrid inverters, which can operate with battery banks and have different operating modes in addition to the standard connection to the electricity grid.
There are already conversations between manufacturers and INMETRO about a new certification model, but there is still no exact date for it to become official.
The second point is the qualification of the Brazilian market. As previously stated, this type of system requires more efficient investigation and more in-depth detailing of projects.
It is very common to hear some installers say that the hybrid system will simply free them from the distribution network, but we know that this will not be the main function of this equipment.
Despite these barriers, hybrid inverters are a natural evolution of the photovoltaic energy market and will certainly bring new business opportunities for manufacturers and design and installation companies, as well as many benefits for consumers, which will be able to count on advanced power management and backup functions.















3 Responses
Just one question, can I hire a conventional ON-GRID system today and later install a HYBRID inverter so that the batteries can supply the lack of energy from the Distributor.
What is the expected time for approval by INMETRO, knowing that they are extremely slow for any more modern solution, in addition to probably being under pressure from the Distributors.
This hybrid inverter will be useful in vacation homes and food trucks.
Can the electrician installing the system commission this system to the same standard as On grid systems? Or do you need a specific qualification for the set?