Energy storage associated with photovoltaic systems has been gaining ground around the world, whether for economic, technical or political-regulatory reasons.
Previously restricted to off-grid systems, battery banks are now an important complement to grid-connected or hybrid photovoltaic systems, which can operate either connected (on-grid) or acting as a backup (off-grid).
Many manufacturers on the market have been working to provide equipment and solutions for hybrid systems, including inverters and lithium battery banks with BMS (battery management system).
A small parenthesis is in order here: what are hybrid systems? Two definitions are commonly used in the market and they get a little confused.
A hybrid system can be one that operates in two different modes: on-grid or off-grid. On the other hand, a system that uses different energy sources or mixes some source (such as solar photovoltaic) and electric batteries can also be a hybrid.
In some cases, the systems are hybrid in every sense: they use batteries for storage, mix different energy sources and have different modes of operation.
Hybrid energy systems are already a reality on any imaginable scale: from microgeneration to centralized electrical energy generation.
In centralized generation, so-called BESS (battery energy storage systems) are already used, which allow the regulation of the intermittency of energy generation, help control the stability of the electrical system or reduce the LCOE (levelized cost of energy) of photovoltaic and wind plants.
At the micro or mini generation level of electrical energy, hybrid systems can perform several functions:
- provide better energy management in homes, avoiding the injection of energy into the electrical grid and prioritizing own generation;
- provide security in commercial facilities through the backup function or by reducing demand during consumption peaks;
- reduce energy costs with the energy shift strategy (storing and injecting energy at scheduled times);
- among other possible functions.
Given the complexity of hybrid systems, which require inverters with different characteristics and operating modes, in addition to lithium battery banks, which require complex BMS systems, hybrid systems are currently going through a market entry phase; which may be more or less advanced in different countries.
Here in Brazil, hybrid systems are already beginning to be used and their use is expected to grow in the coming years due to the factors we mentioned at the beginning of this article (economic, technical or political-regulatory) and also due to the rapid reduction in the cost of batteries in recent years. .
After photovoltaic systems connected to the grid, which have already become widespread in the market and have become popular with consumers (in Brazil and around the world), we now live in a time in which storage systems are showing their potential.
Hybrid systems (like the one in the image below) should become a standard in Brazilian homes in the coming years, as is already happening in other countries.
In Australia, for example, many consumers are prevented from injecting energy into the electricity grid, making it practically mandatory to use battery banks associated with photovoltaic systems.
In Brazil, hybrid systems can allow the consumer to benefit from the white tariff (storing energy to consume at peak times) or avoid injecting energy into the electrical grid if the benefits of the distributed generation credit compensation system are reduced (with the charging of charges for injected energy).
In other words, hybrid systems will enable consumers' long-awaited energy independence, without strings attached or restrictions imposed by companies or regulatory agencies in the electricity sector.

Basically, two solutions for hybrid systems can be found on the market: multiport inverters, which have inputs for energy sources (solar PV, for example) and battery banks; or systems that integrate components in a modular way, as illustrated in the following figure.
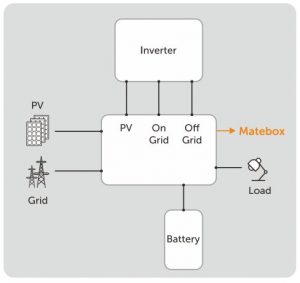
Typically in homes and small systems, one or two multiport inverters may be sufficient. In more demanding or larger systems, the modular solution provided by equipment integration allows greater flexibility and freedom in component sizing.
In the diagram above, the hybrid system is composed of a photovoltaic DC/AC inverter (which can have on- and off-grid outputs, as in the example), a battery system (with built-in DC/AC inverter and BMS system) and an integration panel, which makes connections between devices, power supplies and consumer loads.
The Solax Power solution, which we are exemplifying in this article, allows the integration of all components in an easy and elegant way. A basic cell is made up of a vertical structure that brings together these three components: an on-grid solar inverter (at the top), a Matebox (aggregator box, located in the center) and a bank of lithium batteries (at the bottom).
Through Matebox, multiple vertical columns can be added, with the number of inverters and battery banks required according to the needs of each project.
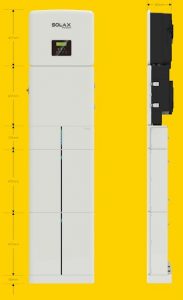
The system illustrated in the figure above employs the following Solax Power components:
- Inverter from the X1 Hybrid G4 family, available in powers from 4.5 kW to 10 kW, three-phase, with on-grid and off-grid operating modes;
- Matebox, for aggregating components without the need for external cabling, providing elegant and fast installations;
- Triple Power 3.0 battery bank.


















3 Responses
Which distributors sell hybrid solar systems in Brazil?
Good morning.
I am an Integrator company and I have a project that combines the On-Grid and Off-Grid systems.
How to contact SOLAR X
Does Solax Power have a national distributor/supplier?