In photovoltaic arrays, different types of electrical configurations can be applied, for example, an array can be formed by just one photovoltaic series, multiple photovoltaic series, multiple photovoltaic subarrays, among other configurations.
All configurations must have overvoltage and overcurrent protection components, in addition to a device that allows the circuit to be isolated.
To connect the cables coming from the photovoltaic series circuits (string) at a single point, an enclosure (box) with a set of direct current buses (positive and negative).
In addition to providing the circuit connections, the string box (technically referred to in Portuguese as a junction box) is where the protection devices and disconnecting switch are also located.
After the connections are unified and pass through the protection devices, the circuit is connected to the inverter.
The norm NBR 16690 Electrical installations of photovoltaic arrays — Project requirements, defines a junction box as: “enclosure in which photovoltaic subarrays, photovoltaic series or photovoltaic modules are connected in parallel, and which can house protection and/or switching devices”.
Casing
The enclosure is the box where the electrical connections, protection devices and switching devices are housed.
The materials require specific protection for each type of environment in which they will be exposed, in addition to protecting the user against electric shock. For this purpose, protection indices (IP) are used.
For indoor environments, the minimum protection index of the string box is IP2X and for external environments, the minimum protection index is IP55.
The image below illustrates an enclosure with IP65 protection, which can be applied in external and internal environments, has UV resistance and flame retardant material. The exemplified system also has a DIN rail and grounding bus.

Overcurrent protection
Overcurrent in a photovoltaic array can be due to ground faults in the array's conductors or short-circuit currents in photovoltaic modules, junction boxes and cabling.
Protective devices are intended to interrupt overcurrents before they become dangerous, due to their thermal and mechanical effects, or result in a temperature rise that is harmful to the insulation, connections, terminations and surroundings of the conductors. For this protection, we use two devices: the fuse and the circuit breaker.
Fuse
gPV type fuses are suitable for use in photovoltaic circuits and offer protection against short-circuit current and overcurrent.
The PV designation refers to the ability of the fuses to operate at DC current with voltage values typical of photovoltaic systems.
To house these fuses in the string box, fuse holders are used that must have a nominal voltage equal to or greater than the maximum voltage of the photovoltaic array and a nominal current equal to or greater than that of the corresponding fuse, in addition to providing an adequate degree of protection for the installation location. and not lower than IP2X.
Fuse holders also protect the user from shocks when accidental contact occurs.
Below we illustrate a 1500 V and 30 A DC fuse holder.

Circuit breaker
The circuit breaker, in addition to protecting against overcurrent, can also operate as a isolating element. Circuit breakers can replace the use of fuses in a photovoltaic system. To do this, it must have an operating current in conventional time of 135% times the nominal current of the device.
The AC type circuit breaker does not have the same insulation and arc interrupting capacity as a DC circuit breaker, therefore, it should not be used in the string box.
The circuit breaker must comply with some requirements:
- Meet IEC 60947-2
- Not being sensitive to polarity
- If sized to isolate full load and potential fault currents from the photovoltaic array and any other connected energy sources, such as batteries, generators and the electrical grid, if present
- Be sized for overcurrent in accordance with item 5.3 of standard NBR 16690
Below we can see a 1500 V and 40 A three-pole DC circuit breaker.

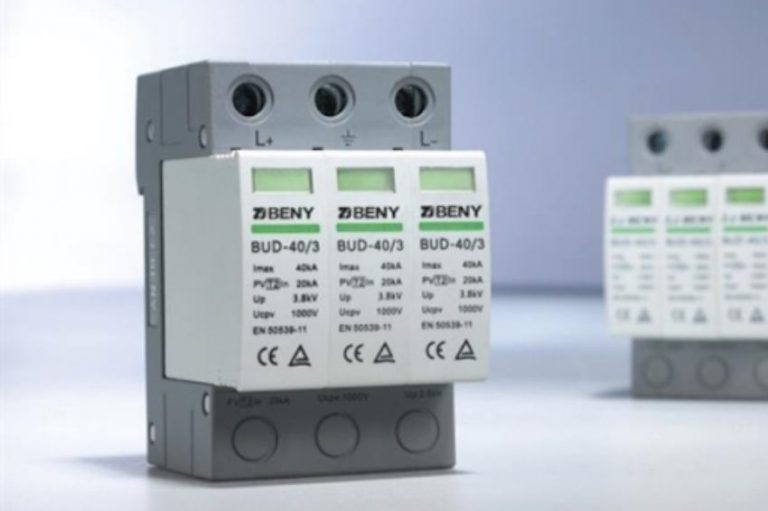
Overvoltage Protection (DPS)
When we talk about DPS (surge protector device) in string box, we usually come across a question: is string box with DPS necessary or not?
The NBR 16690 standard does not specify in which location the DPS must be included, it only says that it must contain an overvoltage device. However, the DPS are subject to maintenance, and when they are internal to the inverter, such maintenance becomes more difficult compared to an external DPS (in the string box)
In this article of Canal Solar, this issue is discussed in more detail. In any case, an overvoltage protection device housed in the string box or inverter protects the inverter from overvoltages originating from the DC system.
The phenomena that can cause overvoltages are: atmospheric discharges in the SPDA (atmospheric discharge protection system) and nearby atmospheric discharges that induce current in the DC circuit.
We have three types of DPS that are defined according to their sensitivity, being specific for each type of operation. Details of an overvoltage device are discussed in more detail in this article from Canal Solar.
Next we check a type 2 DC DPS for 1500V solar photovoltaic application.

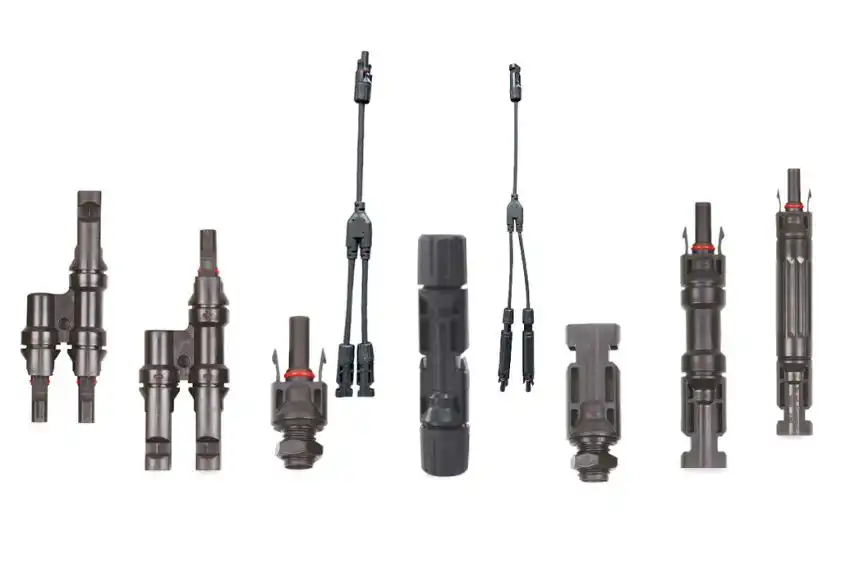
Switching device (disconnector switch)
Switchgear devices are responsible for connecting and disconnecting the DC part of the photovoltaic system. According to the NBR 16690 standard, the disconnector switch must follow some requirements for its operation, namely:
- Do not have any exposed metal parts, whether on or off
- Have a nominal current equal to or greater than that of the respective overcurrent protection device or, in the absence of such a device, have a nominal current equal to or greater than the minimum current capacity required of the circuit to which it is connected
- Not be sensitive to polarity (fault currents in a photovoltaic array can flow in the opposite direction to normal operation)
- Be sized to isolate full load and potential fault currents from the photovoltaic array and any other connected energy sources, such as batteries, generators and the electrical grid, if present
- When overcurrent protection is incorporated, it must be sized in accordance with the overcurrent protections
- Have the ability to interrupt all energized conductors simultaneously
Each project must be prepared respecting the switch's operating voltage and its maximum current, to avoid damage and more serious accidents.
The figure below shows a disconnector switch with 1200 V and 32 A of operation, with an arc suppression of 3ms.

Below we can see a disconnector switch attached to the tables of a photovoltaic park in South Africa, facilitating maintenance maneuvers.

Types of string boxes
The characteristics of the string boxes are directly associated with the configurations of the inverters and photovoltaic arrays.
The number of inputs and outputs of the string box depends on the number of MPPT inputs on the inverter and the number of parallel strings used in the system.
Reading the articles below may be interesting to understand this issue in more detail:
- https://canalsolar.com.br/inversores-com-multiplos-mppt/
- https://canalsolar.com.br/entenda-as-stringboxes-com-multiplas-entradas-e-multiplas-saidas/
Below we can see two string box models with two inputs and two outputs, with operating capabilities at 600 V and 1000 V, respectively.