You full-screen modules are an innovation of DAH Solar for the photovoltaic market. Patented in more than 20 countries, the technology is suitable for use in rooftop or BIPV projects (photovoltaic systems integrated into architecture).

The full-screen photovoltaic module has no frame on the front, just full glass, which provides a more elegant design – in addition to technical advantages.
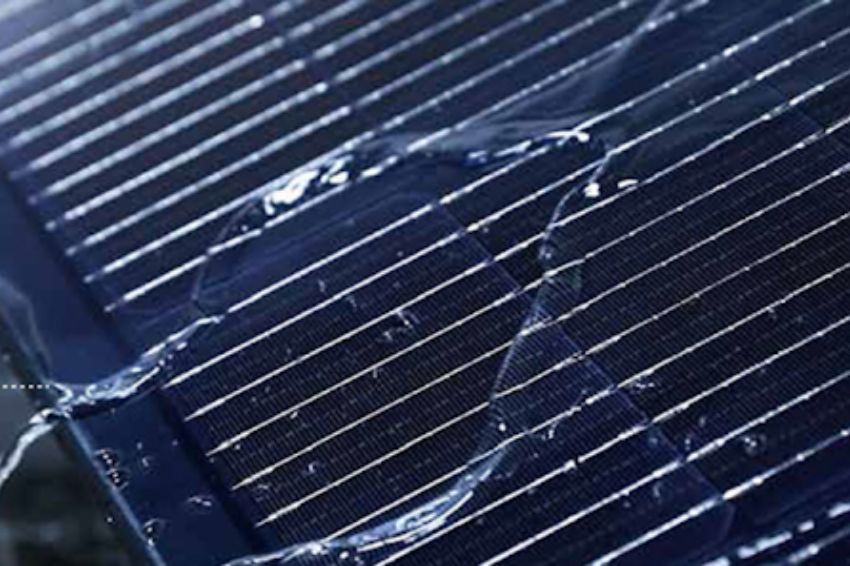
Among the main advantages of full-screen technology is the ability to self-clean the modules. This is possible because the module does not have a visible frame on the front, which prevents the accumulation of dirt and reduces the risk of hot spots, as well as cleaning maintenance costs.
Recently, TÜV Nord published a comparative field test report between 460 W PV modules from DAH Solar – one mono-facial module with full-screen technology and the other half-cell with mono-PERC technology, both with the same dimensions of 1910 x 1134 x 32mm.
The test results showed that the power generation of the full-screen module in relation to that of the conventional mono-PERC half-cell module was 11.5% higher.

This generation gain advantage is characterized by the lower amount of dirt that full-screen modules present in relation to other modules, mainly due to the structure of the module without a front frame, which favors the natural washing of the modules by rainwater. .
The difference that these factors bring, in addition to improving energy generation, is a smaller number of hotspots due to the reduction of the “dirt belt”, a band of dust that normally accumulates near the frame at the bottom of the conventional photovoltaic module.

In Figure 3 it is possible to notice the difference in dirt between a full-screen module and a conventional module.
The tests were carried out in April in Xixia District, Yinchuan, China, and the parameters used in the tests were:
- Fixed module installation angle: 5°
- Exposure to sunlight (pre-test): 60 Wh/m²
- Irradiation: 170.28 kWh/m²
As a result, the full-screen module generated 73.21 kWh of energy and had an accumulated energy generation per watt of 161.17 kWh/kW, while the mono-PERC half-cell module obtained values of 65.06 kWh and 144.54 kWh/kW respectively.
So the comparison showed that the full-screen module was capable of generating 11.5% more energy compared to the mono-PERC half-cell module. Figure 4 illustrates this comparison graphically.
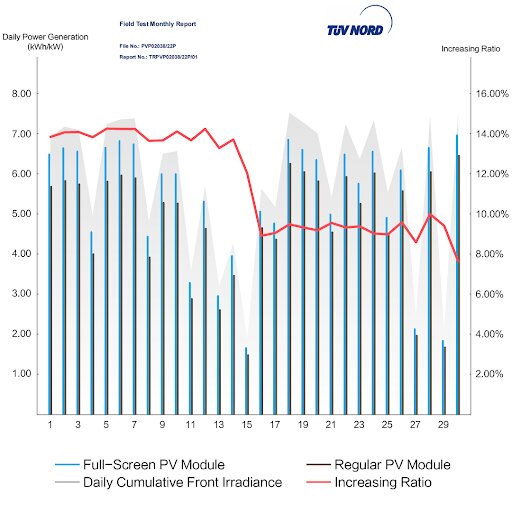
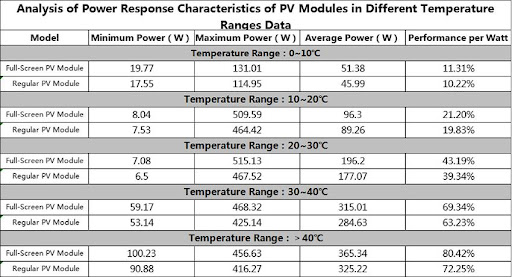
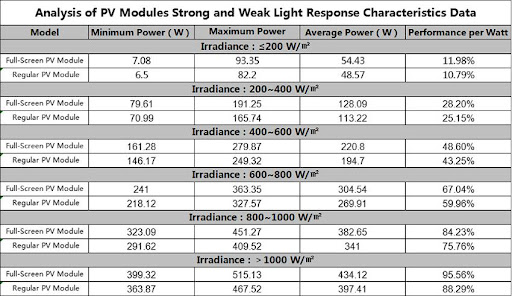
In addition to this comparison between the modules on energy generation, the issue of minimum and maximum power, average and performance per watt of both modules was compared, in different temperature and irradiance ranges, as the following tables illustrate.
References
- DAH Solar Full Screen photovoltaic modules – Helte
- Power Generation Increased By 11.5%! The Full-Screen PV Module Outdoor Field Test Report Published By TüV Nord (dahsolarpv.com)
This article was produced and adapted from technical materials provided by DAH Solar

















One Response
Product manufactured in Brazil?